Stroke Treatment
If you experience stroke like symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately. Seeking stroke treatment can quickly minimize brain damage because permanent brain damage often occurs in the first few hours. Initial treatment focuses on either controlling bleeding for hemorrhagic stroke or increasing blood flow for ischemic stroke . Your physician will perform imaging studies such as a CT Scan or MRI to determine if you have a CVA and the type of CVA it is. Stroke treatment may include medications, surgery, and rehab.
Medication for Stroke Treatment
Medications given will vary depending on the cause of stroke. See the chart below as an example:
CAUSE OF STROKE or SYMPTOM TO BE TREATED: | TYPES OF MEDICATION THAT MAY BE GIVEN: | EXAMPLES (not an exhaustive list) |
Hypertension or High Blood Pressure | Medication to lower blood pressure | Diuretics Beta-Blockers Alpha-Blockers Calcium Channel Blockers ACE Inhibitors Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Vasodilators |
Ischemic Stroke | Thrombolytics (Clot –dissolving medication) | |
Ischemic stroke | Anti-platelet medication (prevent blood from sticking together) | Aspirin Clopidogrel Dipyridamole Ticlopidine |
Ischemic Stroke | Anticoagulants (blood thinners) | Heparin Warfarin |
Swelling in Brain | Hyperosmotic Agents | Mannitol Glycerol Hypertonic Saline Solutions |
High Cholesterol | Medicine to lower cholesterol | Statins |
Note: The above medication information is for educational purposes only and not advice for treatment. Please consult your physician for treatment of stroke.
Surgery
Stroke treatment may include surgery. Again, the type of stroke you experience will determine surgical treatment options. Some surgeries performed may include:
- Endovascular Thrombectomy (EVT) - the blood clot is attempted to be removed by sending a wired-caged device called a stent retriever to the site of the blocked blood vessel in the brain. The stent opens the vessel and grabs the clot which is then threaded back out through the groin or wrist.
- Carotid endarectomy
- Moving or draining blood due to a brain bleed from hemorrhagic stroke
- Brain aneurysm repair
- Repair of arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
Rehabilitation Therapy
After a patient has been medically stabilized, they will begin rehabilitation therapy in an attempt to regain as much function as possible. Therapy is a crucial component of stroke treatment, helping patients to recover lost motor functions, improve mobility, return to activities of daily living (ADLs), overcome communication deficits, and boost cognitive function. By promoting neuroplasticity (or rewiring of the brain), rehabilitation therapies play a vital role in recovery and enhancing the quality of life for stroke survivors. These therapies may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
Physical Therapy
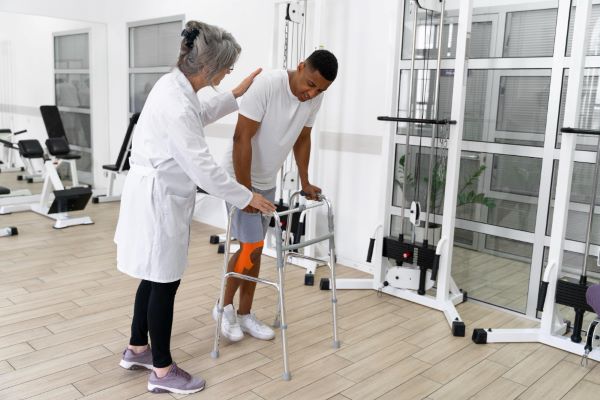

Physical therapy (PT) primarily addresses mobility, strength, and balance issues following a stroke. PT focuses on improving balance and coordination for activities such as sitting, standing, walking, and performing transitional movements used in every day activities such as getting up from bed, moving from bed to chair, moving around the house, and navigating in the community. PT will guide patients in the use of assistive devices for walking or facilitate the transition to a wheelchair for those who can no longer walk. If patients are able, PT will address higher level balance and mobility activities needed to return to work, recreational activities, or sports.
Occupational Therapy
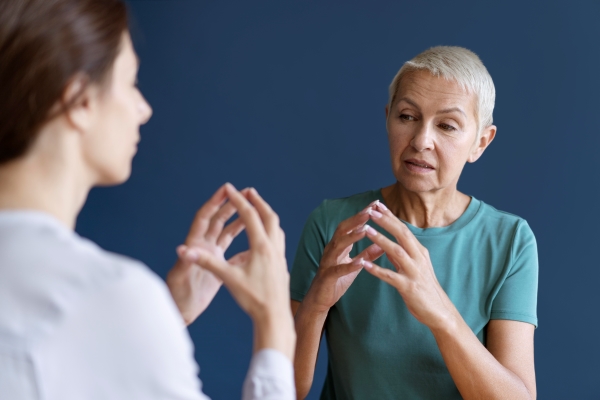

Occupational therapy helps stroke patient regain independence in activities of daily living (ADLs) such as eating, grooming, dressing, toileting, bathing, housework, and recreational activities. Occupational therapists focus on improving movement, activity tolerance, fine motor skills, vision, and cognition so patients can perform self-care and daily activities. If patients are unable to perform daily living skills as before, OTs will teach patients how to use adaptive equipment and techniques to compensate. Specially trained OTs can help with driving and vision rehabilitation.
Speech Therapy

Speech therapy (ST) will provide exercises to improve language and communications skills, swallowing, and cognitive abilities. If necessary, speech language pathologists (SLPs), often referred to as speech therapists may introduce augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices or communication boards to aid patients who struggle with verbal communication. In addition, SLPs will perform swallow studies with patients and make recommendations when a modified diet is needed. This is to ensure that patients with impaired swallowing do not aspirate food and drink which can be dangerous for the patient.
You will find overlap between the various rehabilitation therapies as the effects of stroke are complex often impairing many body functions and not just one single function. The main goal for all rehabilitation therapies is to help a patient maximize their ability to function in everyday life. Therapists will work with a stroke patient and make a rehabilitation plan based on the specific goals of the patient and family.
Learn more out more about specific exercises provided by PT, ST, and OT at our stroke rehab exercises page.
Proper stroke treatment is imperative for the best recovery. Make sure you as a patient or caregiver are aware of all the available treatment options and discuss these options with your physician. Find out more about stroke treatment at https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Stroke
Do You Have a Stroke Treatment Recommendation?
Have you had a good experience with your stroke rehabilitation and treatment? Or maybe you're a therapist who treats stroke with some recommendations. Please share your favorite and most effective stroke rehab exercises or treatment tips below. Please note that submissions from others are for informational purposes only and are not professional medical advice, diagnosis, treatment or care, nor are intended to be a substitute. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider concerning questions you have regarding your health or a loved one's health concerns.
Get Our Stroke Rehab Guide

Our stroke rehab guide is designed specifically for patients and caregivers. It's in pdf format and can be immediately downloaded. It includes about
- Stroke Definition & Causes
- Stroke Treatment
- Rehabilitation Information for Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapy
- Exercise pictures
- Q&A from patients and caregivers
- Adaptive Equipment & Techniques
- How to Prevent Another Stroke & More!
Medical Disclaimer: All information on this website is for informational purposes only. This website does not provide medical advice or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare provider before undertaking a new healthcare or exercise regimen. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment because of something you have read on this website. See the disclaimer page for full information.
- Home
- Stroke Treatment