Submissions from Readers
Vision Problems After Stroke
Vision Testing
(Hoopeston, Il)
Question:If a person is non-verbal, how can they effectively be evaluated for an eye exam? My brother has expressed to me that there may be some vision problems when he sits at our table and looks outside. The expression I am getting from him is that maybe things pass by quickly and are not clear. He had a large stroke 2 months ago, his age is 52.
Answer: Opthalmologists will have training with performing eye exams on individuals who are unable to communicate effectively. I would call before setting an appointment and see if any opthamologists in your area have experience with individuals who have aphasia or have experienced stroke. The more experience the opthamologist has in this area, the easier the exam will be to perform. Specifically a neuro-opthamologist or a neuro-optometrist would be the best fit for your brother's examination.
You can go to https://www.aao.org/find_eyemd.cfm and enter the subspecialty of neuro-opthamology to find an eye M.D. that would meet your needs. If you can't find one in the specific city you live in, enter your state and see if there is a city close to you that has one. If not, you can still call a general opthamologist in your area to see if they have experience with vision testing after stroke.
Vision Rehab Treatment
by Audrey
(Salem, Oregon USA)
Question: What can be done regarding vision rehab in a stroke patient with homonymous hemianopsia who wants to resume driving again?
Thanks, Audrey
Answer:The patient would need to visit a neuro-optometrist (this is a specialized optometrist, not just any optometrist). The neuro-optometrist can evaluate the stroke patient's vision, determine the level of damage, prescribe special glasses that can help with the visual field, and make recommendations about what if any visual rehab is needed. To find a neuro-optometrist in your area, visit the Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Website at https://noravisionrehab.org/ or use their healthcare finder tool at https://nora.memberclicks.net/find-a-provider#/.
Click here to read or post comments
Double Vision
by Diane Takesh
(Oxford NJ)
Question:My sister had a stroke and is now seeing double and it is making her sick to her stomach. Her doctors told her there is nothing she can do for this. I don't believe that.
How likely is it that she will recover doing exercises? Is there other treatments for vision problems after a stroke? Her right eye is turned inward toward her nose.
Answer: Have your sister visit a neuro-optometrist who specializes in working with disorders of the eye from neurologic injury and will be able to help your sister or refer her to a therapist specializing in vision therapy. You could also look around in your area for vision therapy specialists.
If the affected eye muscles have been severely weakened, it will be difficult for that eye to move at the same speed as the other eye, and it becomes difficult to coordinate eye movements together. There are various exercises for diplopia or double vision. I have listed some exercises on the following webpage, www.stroke-rehab.com/eye-exercises.html. You can also find numerous other exercises on other websites and by searching eye exercises or double vision on YouTube. You can check with the MD to make sure any exercises you find are safe and appropriate.
I like to have patients work on coordinating eye movements together as well as patching the stronger eye and working the weak eye on its own. If the double vision is causing nausea and safety issues when moving around, patching one eye can stop the double vision though this is only a temporary solution and a neuro-optometrist may have better solutions such as glasses with prisms or spot patches. You can read about the conditions that neuro-optometrists treat at the Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Association (NORA) Website. Spot patches are discussed at the bottom of that page, and this website has other information that may be of interest to you.
Click here to read or post comments
Mini Stroke and Visual Field Loss
by Fred E.
(Los Angeles, CA)
Question: My 88 year old mother had a small stroke 40 days ago and has lost the vision on the right side of her visual field. She has also lost most of her short term memory. She has no numbness or weakness on either side. Her speech is very clear. No slurring, complete sentences and thoughts. She lives in Eugene Oregon and currently resides in assisted living. She takes herself to the bathroom and uses a walker. She is also on oxygen 1.5 litres. How should we rehab her for the best stroke recovery in Eugene? Thanks.
Answer: I don't know if it's the case with your mother, but stroke patients that do not present with problems such as limb paralysis or impaired speech often do not receive adequate rehabilitation or therapy. Stroke patients whose main deficit is hemianopsia may receive very little or no therapy for the condition because it is often overlooked.
Hemianopsia is the term for when a stroke victim loses 1/2 of their visual field. It can spontaneously improve in the first three to six months following a stroke, however, many do not resolve. Compensation techniques can be used for hemianopsia as well as visual aids. I recommend contacting an opthamologist experienced with hemianopsia as well as finding an outpatient facility with an occupational therapist that specializes in vision training (you will need a MD order for the occupational therapy treatment). When you call the opthamologist or therapy clinic, specifically ask if the professional has experience with treating hemianopsia and their background with treating visual deficits in stroke.
Some of the techniques and equipment used to deal with hemianopsia include:
Saccade training or scanning therapy - This involves training the patient to search or scan into the area of visual field that is missing. Some various activities include head/eye shifts, Dynavision, computerized trainers, descriptive walking, last letter cancellation, puzzles, and search strategies.
Boundary marking - training the patient to search for a marker at the end of a line of text.
Optical devices - special lens that can be used in eyewear such as Gottlieb Visual Field Awareness System, EP Horizontal Lens, and Chadwick Hemianopsia Lens
Visual Restoration Therapy - computer-based treatment that attempts to stimulate existing visual neurons to rewire and make new connections. It is based on the premise of neuroplasticity. Some controversy has surrounded this technique, but it is approved by the FDA.
Eye Does Not Close Fully
Question: What exercises must be done if the eye sticks out a little bit out stroke and does not close fully?
Answer: I would recommend seeing an eye doctor for recommendations. An eye that won't close is prone to dryness and possibly getting debris in the eye. The eye doctor may recommend eye drops or a patch. You could also try some of the exercises that one does when they have Bell's Palsy which paralyzes one side of the face often leaving the eyelid half open. Some of the exercises used can be viewed on this page:
https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/exercises-for-bells-palsy/.
I recommend visiting a therapist who is trained in working with facial muscles so that they can train you to do exercises. You can also read more about vision and eye problems after stroke from this UK document:
Visual Problems After Stroke
How to Use a Computer After a Stroke Causes Left Neglect
by John Camoriano
(Arizona)
My father had a right parietal stroke and now has left neglect. His biggest loss is the inability to use his computer like he once did. Using an excel spread sheet is tough because sometimes he sees the column in the sheet and other times he does not see all the columns.
Are there any tools for a patient to regain use of the computer or to decrease issues related to its use?
Answer: First, I would have a neuro optometrist or neuro-opthamologist examine your father for visual deficits. If there are any visual deficits, they may prescribe special eyewear with prisms or other adaptive lens that can increase the visual field. This is not done by just any eye doctor. You have to see someone who specializes in working with vision impairments from stroke. You could try techniques used with low vision patients such as larger computer text, magnifiers, or screen readers. I would recommend doing a search for computer adaptations for individuals with low vision and see if anything comes up. You can also move the screen further to the right and mark the left side of the computer with a bright colored piece of tape so that your father knows that he has not scanned all the way to the left until he sees that piece of tape.
Tunnel vision from stroke
by Gail
(Wellsburg, Iowa)
Question: My husband suffered a stroke that only effected his eye sight. It left him with tunnel vision. He says he can see everything upward but out to the sides and especially below he says there is nothing.
Would occupational therapy help him in any way? The doctors never really followed up with what he was suppose to do, they just sent him home.
Answer:You can take your husband to a neuro-optometrist that deals with special vision issues like this which are due to stroke. Often special glasses with prism lenses can be made to help with the vision deficit. They may also have visual therapy available as well or at least will be able to refer you to a therapist. A neuro-optometrist is different than your regular optometrist, and to find the closest one to where you live, you can go to https://nora.memberclicks.net/find-a-provider#/. It looks like the closest two to you are in Independence and Cedar Rapids. There are not many neuro-optometrists so I would just enter your state name when you search rather than your city.
How to Improve Left Visual Field
by Ray
(Hibbing, MN, USA)
Question: I have a left visual field deficit following a hemorrhagic stroke on the right side What can I do to reduce the deficit?
Ray
Answer:If you have lost part of your visual field, you may need special glasses to help. There are glasses with prisms that might be beneficial. You would need to see a neuro-optometrist who specializes in visual problems due to neurological conditions such as stroke. This is a very specialized field. In order to find a neuro-optometrist in your area, you can visit the Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Association website referenced above with link in previous questions. Make sure you select to find a neuro rehabilitation optometrist when doing your search. You can also search for therapists who do vision rehab.
Optic Nerve Damage
by Omran Khalaf
(Pensacola Fl)
Question:Is it possible to improve visual field after five years of glaucoma and a stroke? My optic nerve had a considerable damage before the stroke now I can hardly see with my right eye.
Answer: I believe that damage to the optic nerve caused by injury or disease tends to be permanent. My understanding is that the cells that form the optic nerve don't regenerate or repair themselves, however, I know that there is always new discoveries and research occurring so it would be best to check with an opthalmologist or optometrist for the best answer to your question.
Left Side Neglect Due to Right Parietal Hemorrhagic Stroke
Question: During inpatient speech therapy my husband was given written exercises to help him visually scan the left side. He has left sided neglect. Can you give me a website that I can download some written activities for him to do
Answer: I would recommend reading some of the eye exercises I have on my website at https://www.stroke-rehab.com/eye-exercises.html. On that page I recommend two websites, www.eyecanlearn.com and www.lumosity.com. There are also apps for visual neglect. One can be found at http://tactustherapy.com/app/vat/. As far as a website where you can find worksheets, you could try:
https://edhelper.com/visual_skills.htm
https://www.printablesfree.com/categories/visual-scanning-worksheets
https://www.yourtherapysource.com/freestuff.html (look under the visual perceputal freebies section)
Many education websites have worksheets. You can google visual scanning worksheets which will will probably pull up quite a few websites for you. You could also look up visual neglect worksheets. There are also many apps available for this as well.
Vision Problems - Fourth Nerve Palsy
by Christina
(Caledon, ont)
Question: I had a stroke 2 years ago and have blurry vision, double vision, was told maybe 4th nerve palsy problem.... is there a specialist that can operate or what is the best treatment?
Answer: Some treatments for 4th nerve palsy include prism glasses to bring the double images together as one image, eye patching, botulinum toxin injection, and surgery to realign the eyes to get rid of double vision. You would need to consult with an ophthalmologist or neuro-opthalmologist for treatment.
Vision Problems: Fixed Objects in Vision
by Karla
(Greenwood, IN)
Question: Have you had ANYONE report having permanent visual "objects"? About six months after my stroke I started having symptoms of vitreous detachment but no actual detachment was found. A few months after that, I began developing what my ophthalmologist calls "incomplete hallucinations", meaning that I see shapes as tho they are on the inside of a pair of contact lenses. The shapes are different sizes but they are all perfect black circle with a perfect black ring around them (think the Target store symbol). There are hundreds of them in each eye; more in the right than the left, they are always there in the same places and they move with my eyes without any lag time like a floater would have. I do have one fairly large floater in my left eye but that's the only one. According to my ophthalmologist at the Low-Vision Center, these are NOT floater and they are not physiological to my eyes themselves; they are neurological. Please tell me you have heard of this before because most people think I'm nuts. Thank you.
Answer: I have not had a patient express a specific shape they are seeing, but I have definitely had patients with visual changes, blind spots, dark spots in their vision, and visual hallucinations. I would suggest seeing a neuroptometrist who specializes in visual problems due to neurological conditions such as stroke (this is a very specialized area - not a regular optometrist). You can find one of these specialists by visiting the Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Association website.
Eye Test
by Sheena
(Leicester)
:Question: I was advised to have an eye test by my doctor as he said peripheral vision can be affected by stroke.
I failed the peripheral vision test although my eye test was fine, and my prescription did not change. Other tests for eye health for glaucoma and such were fine.
I am now very nervous about going back, although I told people I failed the test and and was retested and came through with flying colours at the Optician's office.
I wonder how many people fail this test completely after a stroke as I am very nervous about going back for the test although I feel very confident of my ability to drive.
Answer : I would advise you to go to a neuro-optometrist which is a specialist that deals with vision changes after stroke. Sometimes prisms can be put in glasses to restore peripheral vision. There are a limited number of neuro-optometrists and they are not the same a general optometrist or optician, so make sure you are seeing the right specialty. It is very important to make sure your peripheral vision is intact or adequate for driving as you may pass a regular exam without difficulty but still lack peripheral vision which is important for changing lanes and seeing cars that are next to you or seeing pedestrians. I am not sure if they have neuro-optometrists in the UK, but you could also see a neuro-opthamologist or ask your optometrist. I would call and specify what you need evaluated and ask if they do prisms for glasses to improve peripheral vision.
Click here to read or post comments
Blind in right eye
by John Boyt
(Gig Harbor, Wa)
Question: I am blind in my right eye. On a scale of 10, I have 1/2 of 1 site on my right side of my eye. I spent 1 day in emergency care I have seen a Optician and ordering a prosthetic soft contact to stop my retina from getting so much light and getting headaches. is there any exercises that will work since I cant see out of the right Eye. Thank You.
Answer: If you have had sight changes after stroke, it is best to see a neuroptometrist that specializes in vision disorders after stroke. Sometimes they can order special glasses that can help with hemianopsia and other vision disorders related to stroke that a regular optometrist does not typically deal with or may miss. You can find a neuro optometrist on the www.noravisionrehab.org website or at https://nora.memberclicks.net/find-a-provider#/
Blurry vision and tearing
by Elaine Samaniego
(Lawndale, CA)
Question: I am sure my guy had a stroke on Thursday evening today is Sunday, and he won't go to doctor. Since this happened his right eye is tearing and he can't see. I have asked him every day if he will go get checked but his answer is no. What should I do?
Answer: I wouldn't speculate, but I definitely would see someone regarding the changes in vision. Sudden vision changes can be a sign of stroke,but since you indicate his symptoms only seem to be involving his eyes, and he won't go to the hospital, I would encourage you to have him visit an eye doctor right away. If the eye doctor suspects something is going on neurological such as a stroke, then the doctor will inform your significant other and can let him know that he needs to see a neurologist or go to the hospital.
The eye doctor may find something specifically wrong with only the eyes that he can treat. Plus if it is something specific to the eyes, an eye doctor will have special equipment to examine the eyes. Sometimes vision problems need to be treated right away to prevent vision loss, so you could let him know that he better see an eye doctor right away to protect his vision.
Eye Tracking Issues
by Jim Smullen
(Houston Texas)
Question: Four months ago I suffered two brain aneurysms and am now out of the hospital. I have tracking issues in my left eye. However, it has gotten a lot better. With 1 being the worst and 10 the best, my tracking issue is now at 8. What besides the Brock string is good for tracking?
Answer: You can look under the eye exercises tab on the stroke-rehab.com website for some further ideas. One simple thing you can do is move your finger around as you watch the tip. I often have patients do one eye at a time (one eye closed) and then with both eyes open. There are phone apps and computer games that can be used to work on eye-tracking. A couple of computer sites are lumosity.com and eyecanlearn.com. To find a phone app, just search eye tracking exercise app or eye exercise app, and many will pull up.
Cloudy vision after stroke
by Melissa
(Reno, NV)
Question: My mother had a stroke 1 yr ago. It caused partial loss of vision on her right side. During a 4 day road trip, her vision would get cloudy and she has to wipe her eyes. This continues while watching TV at home. Should we be worried?
Answer: Strokes can definitely cause vision issues, but it sounds like from your question that the blurry vision is a recent development that did not originally occur with the stroke she had a year ago. She would need to see an eye doctor to determine the cause. Many issues can cause blurry vision including cataracts, age-related changes, eye strain from TV/computers, dry eyes, infection, and stroke to name a few.
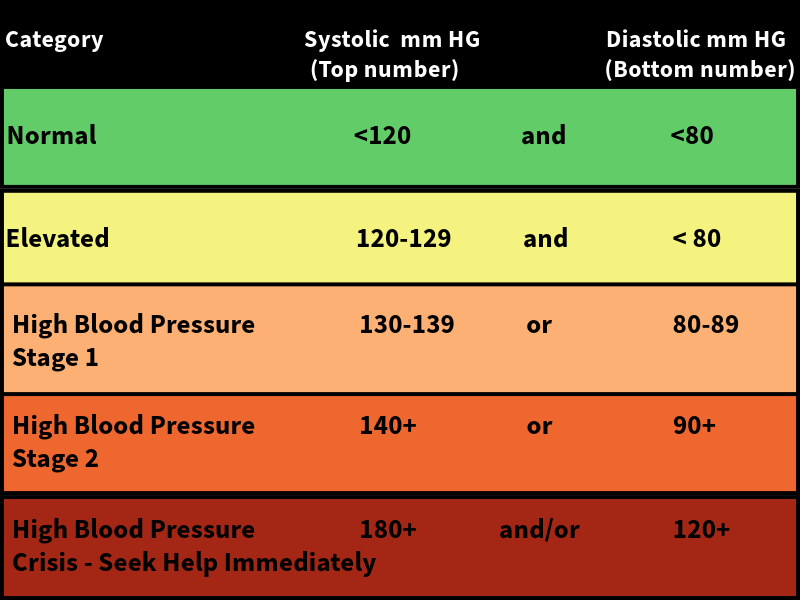
If the blurry vision appeared suddenly and especially with any other symptoms (such as a decline in cognition/speech, weakness, unsteady balance, headache, high blood pressure, etc.) then you would want to get her to the doctor or ER right away to make sure she isn't having another stroke. If unsure, it's always better to err on the side of caution. Whatever is going on could range from something less serious to something very serious especially considering she has a history of stroke. There is no way to know unless she goes in to get diagnosed.
Stroke can occur that only leads to changes in one area such as vision, so other symptoms do not have to be present. That is another reason it is important to be seen by a doctor. Strokes go undetected sometimes because people think there has to be a myriad of symptoms that occur, but that is not always the case. I've definitely seen strokes that only cause eye changes and not other noticeable symptoms. It's not as common, but it definitely can happen.
Click here to read or post comments
Treatment Tips from Others
To see tips from other survivors and caregivers about their treatment recommendations, click here.
Get Our Stroke Rehab Guide

Our stroke rehab guide is designed specifically for patients and caregivers. It's in pdf format and can be immediately downloaded. It includes about
- Stroke Definition & Causes
- Stroke Treatment
- Rehabilitation Information for Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapy
- Exercise pictures
- Q&A from patients and caregivers
- Adaptive Equipment & Techniques
- How to Prevent Another Stroke & More!
Medical Disclaimer: All information on this website is for informational purposes only. This website does not provide medical advice or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare provider before undertaking a new healthcare or exercise regimen. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment because of something you have read on this website. See the disclaimer page for full information.
- Home
- Stroke Questions
- Cloudy vision after stroke